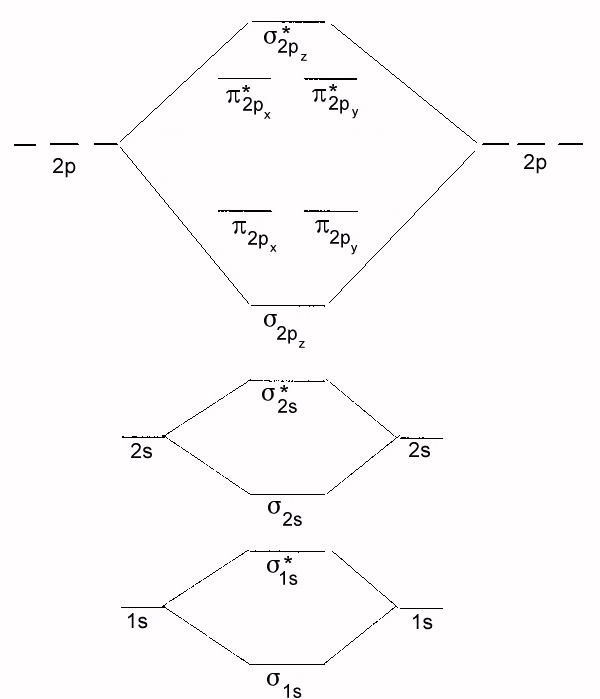
Using the diatomic molecular orbital scheme above, tell the bond order of the diastmic species below and whther they are diamagnetic or paramagnetic. (10 points)
- NO+, B.O. = 3, diamagnetic
- BC, B.O. = 1.5, paramagnetic
- CF2-, B.O. = 1.5, paramagnetic
- Li2, B.O. = 1, diamagnetic
- C2, B.O. = 2, paramagentic
- V = [Ar]4s23d3
- Br = [Ar]4s23d104p5
- Ba = [Xe]6s2
- Nd = [Xe]6s24f4
- Te = [Kr]5s24d105p4
- Cr = [Ar]4s13d5
- Ag = [Kr]5s14s10
- Gd = [Xe]6s24f75d1
- Pd = [Kr]5s04d10
- Au = [Xe]6s14f145d10
- V, n = 3, l = 2, ml = 0, ms= +1/2
- Br, n=4, l=1, ml=0, ms= -1/2
- Ba, n=6, l=0, ml=0, ms= -1/2
- Nd, n = 4, l = 3, ml = 0, ms= +1/2
- Te, n = 5, l = 1, ml = -1, ms= -1/2
- Cr, n = 3, l = 2, ml = 2, ms= +1/2
- Ag, n = 4, l = 2, ml = 2, ms= -1/2
- Gd, n = 5, l = 2, ml = -2, ms= +1/2
- Pd, n = 4, l = 2, ml = 2, ms= -1/2
- Au, n = 5, l = 2, ml = 2, ms= -1/2
-
Pauling' rules: Difference of 0, non-polar covalent bond; Difference between 0 and 1.7, polar covalent bond; Difference greater than 1.7, ionic bond
- Al-C, 2.55 - 1.61 = 0.94, polar covalent bond
- H-H, 2.20 - 2.20 = 0, non-polar covalent bond
- Hg-H, 2.20 - 2.00 = 0.20, very slightly polar covalent bond
- Sc-Cl, 3.16 - 1.36 = 1.8, ionic bond
- K-Cl, 3.16 - 0.82 = 2.34, ionic bond
- orbital - A three dimensional area of space within which there is a finite possibility of finding the electron.
- first ionization energy - the energy necessary to remove the outermost electron of an atom. It is usually expressed in kJ/mol.
- electron affinity - the enrgy released when an atom captures an electron to become an anion. It is usually expressed in kJ/mol.
- isoelectronic - A word meaning "having the same electron configuration."
- quantum number - A number expressing a certain allowed energy state.
- Heisenberg uncertainty principle - The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that you cannot know the momentum and the position of a subatomic particle such as the electron to within a certain amount, designated by the equation:
ΔxΔp = h/2π
- deBroglie relationship - A relationship which relates the momentum of particles of matter to a wavelength. This introduced the idea that matter has wave-like properties. The relationship is λ = h/mv .
- photon - A single quantum of light (first proposed by Einstein who postulated particle-like properties for light, by proposing that its energy was packaged in quanta he called photons).
- period - A period is a horizontal row on the periodic table.
- group or family - A group or family is a vertical column on the periodic table.
- SeF4
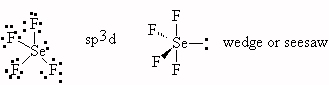
- BeF2
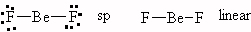
- PBr3
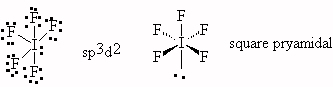
- IF5
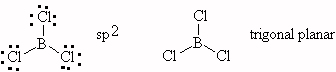
- BCl3
- Li or K
- P3- or V5+
Mg or S
- Mn2+ or Mn4+
- C or Ne
- Bi, Bi3+ and Bi5+
- Fe, Fe2+ and Fe3+
- Sn, Sn2+ and Sn4+
- As, As3+ and As5+
- Pb, Pb2+ and Pb4+
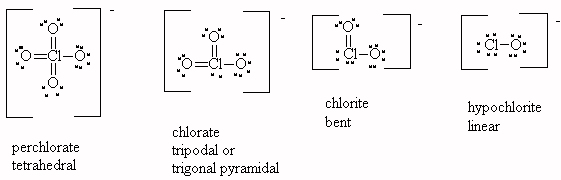
The fewer lone pairs on chlorine, the more acidic the acid in the perchlorate series. Since perchlorate has no lone pairs on chlorine, HClO4 is the most acidic of the series. Hypochlorite has the most lone pairs on chlorine (3 lone pairs), hence HClO is the least acidic of the series.