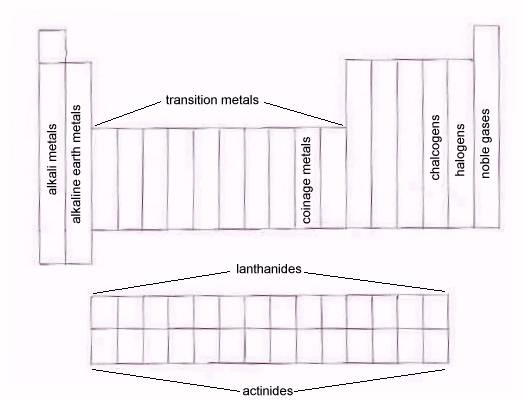
- PBr3, tripodal, sp3
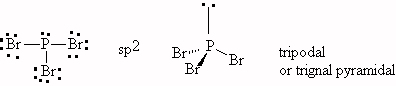
- CCl4, tetrahedral, sp3
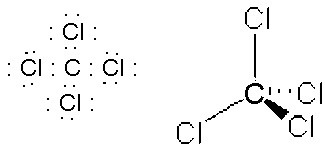
- NH3, tripodal, sp3
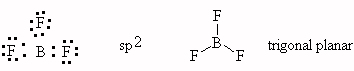
- BF3, trigonal planar, sp2
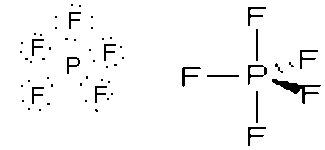
- PF5, trigonal bipyramid, sp3d
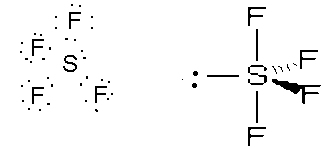
- SF4, wedge, sp3d
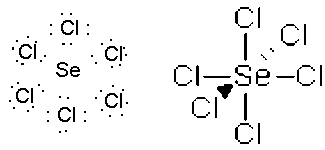
- SeCl6, octahedral, sp3d2
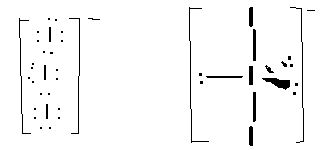
- I3-, linear, sp3d
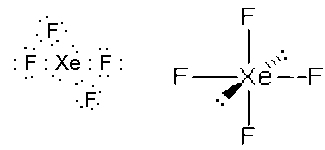
- XeF4, square planar, sp3d2
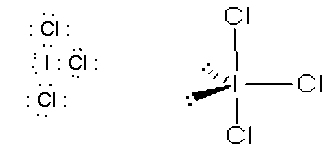
- ICl3, t-shaped, sp3d
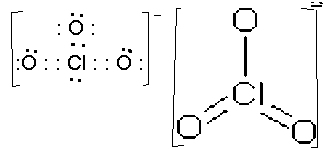
- ClO3-, trigonal planar, sp2 plus d orbital interactions in p bonds. Only one of three possible resonance structures is shown.
- MnSO4 manganese (II)sulfate
- AlPO4 alluminum phosphate
- P2O3 diphosphorus trioxide
- K3PO4 potassium phosphate
- KClO3 potassium chlorate
- Sc2S3 Scandium (III) sulfide
- N2O5 dinitrogen pentoxide
- Ca(NO3)2 calcium nitrate
- CoNO3 cobalt (I) nitrate
- FeSO4 iron (II) sulfate
- hydrazine
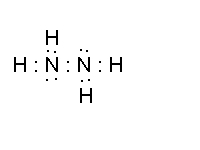
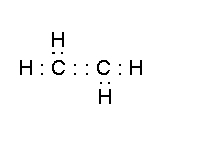
- ethylene
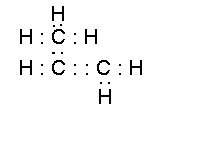
- propylene
- valence electrons - reactive electrons above the previous noble gas, likely to participate in bonding
- bonding pair of electrons - a pair of electyrons shared between two atoms to form a bond
- lone pair or non-bonding pair (electrons)- a pari of electrons resident on an atom that does not participate in bonding
- electronegativity - the attraction an element has for the electrons in a bond with a different element
- first ionization energy - the energy needed to remove the outermost electron of an atom
- quantum number - a number designating an allowed energy
- n - prinicpal quantum number, n = 1, 2, 3,...
- l - angular momentum (azimuthal) quantum number, l = 0 to n -1
- ml - magnetic quantum number, ml = -l to +l
- ms - spin quantum number, ms = +1/2 or -/12
- Pauli exculsion priciple - each electyron in an atom, ion or molecule has a unique set of quantum numbers
- Hund's rule - electrons are placed in orbitals with the same (degenerate) energies with parallel spins prior to pairing electrons in orbitals
- periodicity - the property that similar chemical properties recur within the periodic table. Such properties lead to groups or families (vertical columns) on the periodic table.
- period - a horizontal row on the periodic table.
- group or family - a vertical column on the periodic table.
- isoelectronic - having the same electron configuration.
- paramagnetic - containing at least one unpaired electron.
- diamagnetic - containing no unpaired electrons.
- O and Li
Li2O
- P and S
P2S3 or P2S5
- S and F
SF2, SF4 or SF6
- Al and F
AlF3
- Mg and N
Mg3N2
- Mn = [Ar]4s23d5
- Se = [Ar]423d104s2
- Pr = [Xe]6s24f3
- Pb = [Xe]6s24f145d106p2
- As = [Ar]4s23d104p3
- Sr = [Kr]5s2
- In = [Kr]5s24d105p1
- He = 1s2
- Mg = [Ne]3s2
- Sc = [Ar]4s13d1
- n = 3, l = 2, ml = 2, ms = +1/2
- n = 4, l = 1, ml = -1, ms = -1/2
- n = 4, l = 3, ml = -1, ms = +1/2
- n = 6, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +1/2
- n = 4, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +1/2
- n = 5, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = -1/2
- n = 5, l = 1, ml = -1, ms = +1/2
- n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = -1/2
- n = 3, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = -1/2
- n = 3, l = 0, ml = 3, ms = +1/2
- paramagnetic
- paramagnetic
- paramagnetic
- paramagnetic
- paramagnetic
- diamagnetic
- paramagnetic
- diamagnetic
- diamagnetic
- paramagnetic>
- Cr = [He]4s13d5
- Gd = [He]6s24f75d1
- Au = [He]6s14f145d10
- Pd = [Kr]5s04d10
- Mo = [Kr]5s14d5
Increases traveling up a columns and increasing the farther right in a row, for the s and p blocks. For the d and f blocks a chart needs to be consulted.
.
Increases traveling up a columns and increasing the farther right in a row.
Increases traveling up a columns and increasing the farther right in a row for the absolute value of the electron affinity.
- If the formula for the oxide of aluminum is Al2O3, what would the formula for the oxide of indium, In, be?
In2O3
- If the formula for the sulfide of beryllium is BeS, what would the formula for the sulfide of strontium, Sr, be?
SrS
- If the formula for the nitride of sodium is Na3N, what would the formula for the phosphide (P3-) of sodium be?
Na3P
- If the formula for the fluoride of of zinc is ZnF2, what would the formula for the fluoride of cadmium, Cd, be?
CdF2
- If the formula for the oxide of titanium is TiO2, what would the formula for the oxide of zirconium, Zr, be?
ZrO2
- CH4
covalent
- Na2S
ionic
- SO3
covalent
- Na2SO3
ionic
- MgH2
ionic
- P2S3
covalent
- BF3
covalent
- AlBr3
ionic
- SeO2
covalent
- CO2
covalent
- ClO4-
cl + 4(-2) = -1
cl - 8 = -1
cl -8 + 8 = -1 + 8
cl = +7
- P2O3
oxygen wants two electrons, so o = -2
- Fe2(SO4)3
2(fe) + 3(-2) = 0
2(fe) - 6 = 0
2(fe) - 6 + 6 = 0 + 6
2(fe) = +6
fe = +6/2 = +3
- PPF5
p + 5(-1) = 0
p - 5 = 0
p - 5 + 5 = 0 + 5
p =+5
- ClO2-
cl + 2(-2) = -1
cl - 4 = -1
cl - 4 + 4 = -1 + 4
cl = +3
- SnS2
sn + 2 (-2) = 0
sn - 4 = 0
sn - 4 + 4 = 0 + 4
sn = +4
- PO43-
p + 4(-2) = -3
p - 8 = -3
p -8 + 8 = -3 + 8
p = +5
- ClO-
cl + -2 = -1
cl + -2 + 2 = -1 + 2
cl = +1
- Li3N
N would like to gain three electrons, so -3.
- CO32-
c + 3(-2) = -2
c - 6 = -2
c - 6 + 6 = -2 + 6
c = +4